The Google Search team have been busy making big changes to Google Search Console (GSC), an essential free tool for webmasters to monitor how their website is performing within Google Search. An essential part of any SEO toolkit, Google had began rolling out a brand new version of Search Console in the past few weeks. It should now be live for everyone, although it’s still very much in Beta. As part of our SEO services for hotels, we at Travel Tripper use Google Search Console extensively, so we wanted to share our findings on what has changed.
A work in progress
So far, it seems best to consider this as a completely revamped version of GSC—there’s a range of new insightful features that have been announced, but as of writing there’s not a whole lot of new features publicly available.
Google said that the old version of GSC will remain live (which you can find via this link) and should be used in tandem with the newer version, while they continue to roll out new features. In short, the newest version isn’t the final product, and the old version will still be required for the bulk of SEO work.
John Mueller, Webmaster Trends analyst at Google is very publicly looking to SEO specialists to provide feedback and assistance to their team with regard how they use GSC currently, and what additional features they’d like to see. To us (at least on the surface) Google appear willing to take direct feedback from their users and listen to their suggestions, so this “more open” relationship with the webmaster community may indicate that the latest version will be more flexible in its offering.
The Index Coverage Report
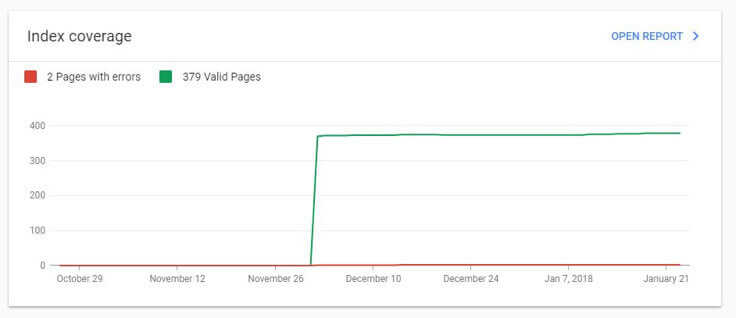
The new Index coverage report is so far receiving rave reviews from SEO experts, and from the Google Search community forums it’s clear that this was a feature many webmasters had been requesting for a while. The new Index coverage report now shows much more specific data regarding the index status of your website’s pages. Whereas the old version of GSC would simply tell you when crawl errors occurred and on which pages (when Google’s search crawler couldn’t successfully crawl a page), the new version gives far more insight into why, whether it was due to the page being redirected elsewhere, a 404 page error, soft-404s, the existence of “noindex” tags, and so on.